MuleSoft, a widely used integration platform, provides flexibility in choosing between shared and dedicated load balancers based on specific use cases, requirements, and performance considerations. Let’s explore the differences between MuleSoft shared and dedicated load balancers:
Shared Load Balancer:
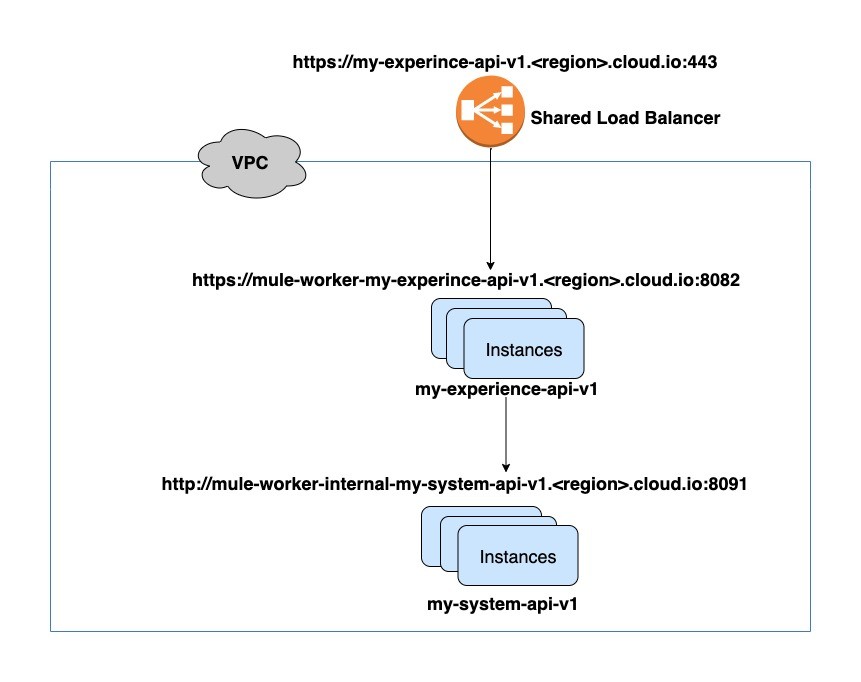
1. Cost-Effective:
- Shared load balancers are a cost-effective solution for small to medium-sized projects where dedicated resources might be overkill.
- Multiple applications or services share the same load balancer infrastructure, reducing overall costs.
2. Resource Sharing:
- Resources are shared among different applications or services, making it an efficient choice for scenarios with moderate traffic.
3. Ease of Management:
- Shared load balancers are often easier to set up and manage since the infrastructure is shared and maintained by the platform provider.
4. Scalability:
- Shared load balancers might have limitations in scalability, making them suitable for projects with predictable and moderate traffic.
5. Default Option:
- MuleSoft CloudHub, a cloud-based integration platform, often uses shared load balancers by default for its applications.
Dedicated Load Balancer:
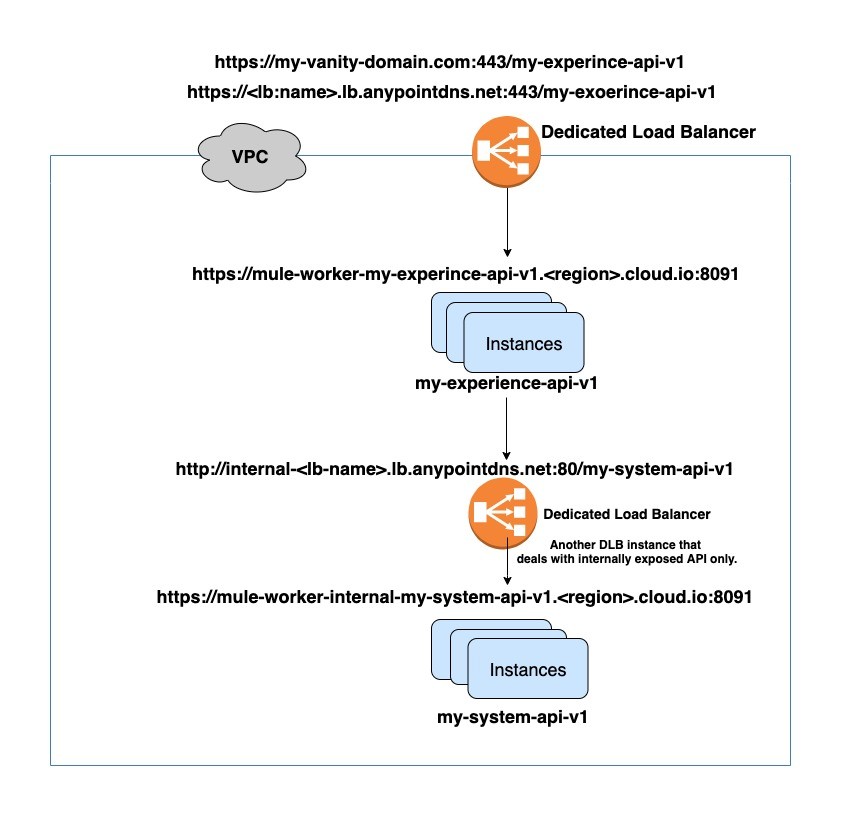
1. Isolation:
- Dedicated load balancers offer isolation, providing dedicated resources for a specific application or service.
- Isolation ensures that the performance of one application does not impact others, making it suitable for critical or high-traffic scenarios.
2. Customization:
- Users have more control over the configuration and customization of a dedicated load balancer, tailoring it to specific performance and security requirements.
3. High Performance:
- Dedicated load balancers are designed to handle higher loads and provide better performance compared to shared alternatives.
4. Security Considerations:
- In scenarios where security and compliance are top priorities, a dedicated load balancer might be preferred due to the enhanced control over security settings.
5. Scalability:
- Dedicated load balancers offer better scalability options, making them suitable for large-scale projects with varying traffic patterns.
Considerations for Choosing Between Shared and Dedicated Load Balancers:
- Traffic Patterns:
- Evaluate the expected traffic patterns for your applications. If you anticipate varying or high traffic, a dedicated load balancer might be more suitable.
- Resource Requirements:
- Consider the resource requirements of your applications. Critical or resource-intensive applications may benefit from dedicated resources.
- Cost and Budget Constraints:
- Assess your budget constraints. Shared load balancers are more cost-effective, making them suitable for projects with budget constraints.
- Security and Compliance:
- If security and compliance are top priorities, a dedicated load balancer provides more control over security settings and isolation.
- Ease of Management:
- Evaluate the complexity of management. Shared load balancers are often easier to set up and manage, while dedicated load balancers offer more customization but may require more effort.
In summary, the choice between shared and dedicated load balancers in MuleSoft depends on the specific requirements, budget constraints, and performance considerations of your integration projects. It’s essential to carefully assess your project’s needs to make an informed decision.

Vinod
January 12, 2024Test
shiv
January 12, 2024test
Vinod
January 12, 2024Testing
shivangi
January 12, 2024sss